KnockoffGWAS
KnockoffGWAS is a powerful and versatile statistical method for the analysis of genome-wide association data with population structure.
Overview
KnockoffGWAS localizes causal variants precisely, controlling the false discovery rate even if the samples have diverse ancestries or close familial relatedness. This method is equally valid for quantitative and binary phenotypes, making no assumptions about their genetic architectures. Instead, we rely on hidden Markov models for the distribution of haplotypes.
For more information, read the accompanying paper:
FDR control in GWAS with population structure
M. Sesia, S. Bates, E. Candès, J. Marchini, C. Sabatti
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2021; doi:10.1073/pnas.2105841118
For an earlier version of KnockoffGWAS restricted to homogeneous populations, see also KnockoffZoom.
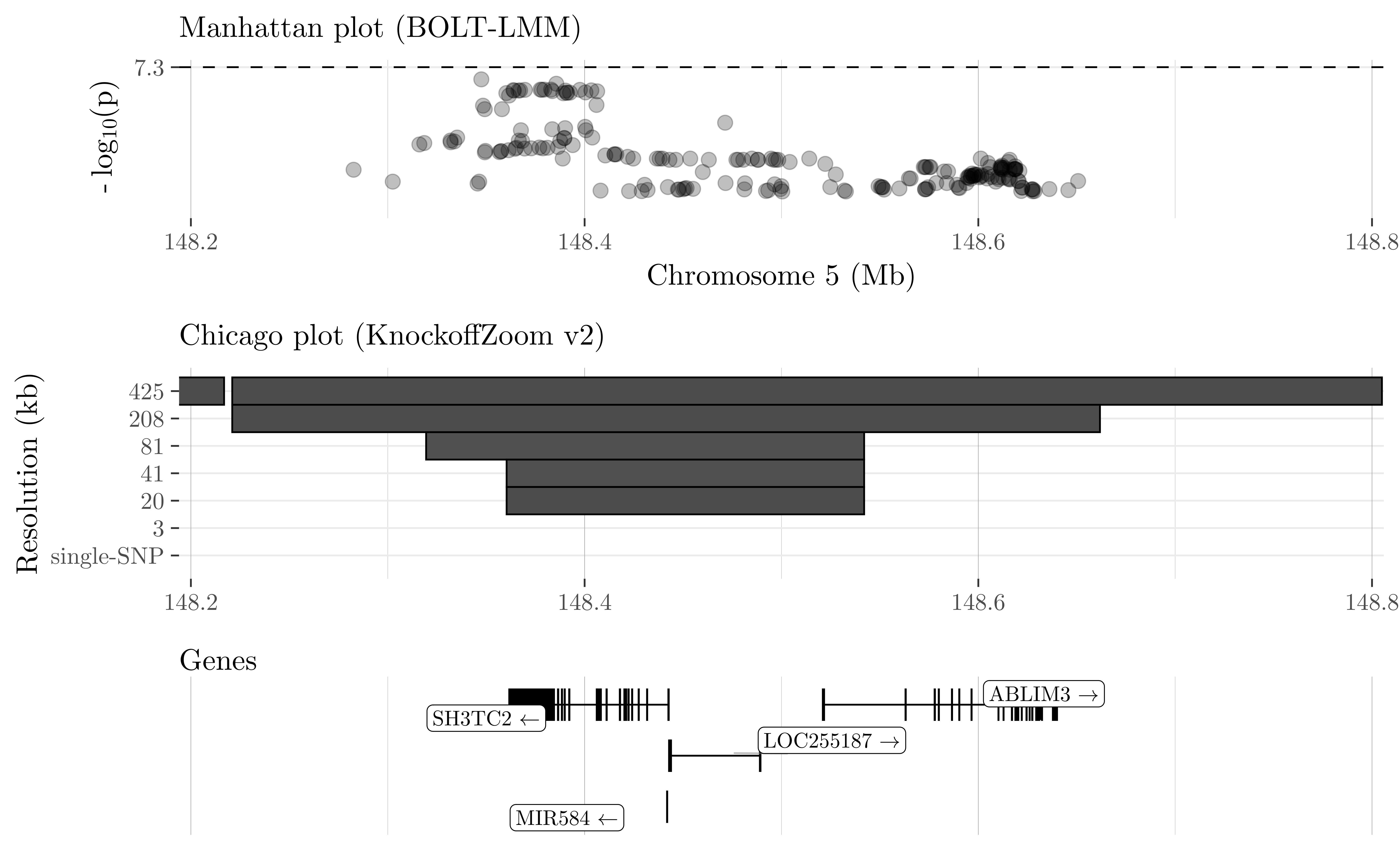
We partition the genome into contiguous LD blocks and test whether the trait is independent of the SNPs in any block, conditioning on the others. The resolution of the hypotheses is determined by the size and homogeneity of the LD blocks, which we choose in advance. To balance power and resolution, we consider multiple partitions, starting with a coarse view and successively refining it. Some of the results obtained at different resolutions for cardiovascular disease in the UK Biobank are visualized below.